StoryboardTo3D: AI Scene Positioning
An Unreal Engine plugin I built that uses AI vision models to automatically position 3D assets based on storyboard images. My MS Thesis research discovered a 37% gap between AI confidence and actual accuracy.

Storyboard input

3D scene output
The Problem
Storyboards are still how animation and game pre-production starts, but turning 2D sketches into 3D scenes is tedious. Someone has to look at a flat drawing and figure out where everything goes in 3D space. Studios approve a storyboard, say "move forward," then don't see the actual 3D result until weeks or months later. By then they've spent the money. If the scene doesn't read the way they imagined, it's too late to pivot without blowing the budget.
Depth is Ambiguous
Multiple 3D setups can look identical from one camera angle. A character 50 units away vs 150 units away might look like they're in the same spot from the storyboard view.
AI Doesn't Get Sketches
Vision models train on photos. Storyboards have loose lines and stylization that confuses them.
The Solution
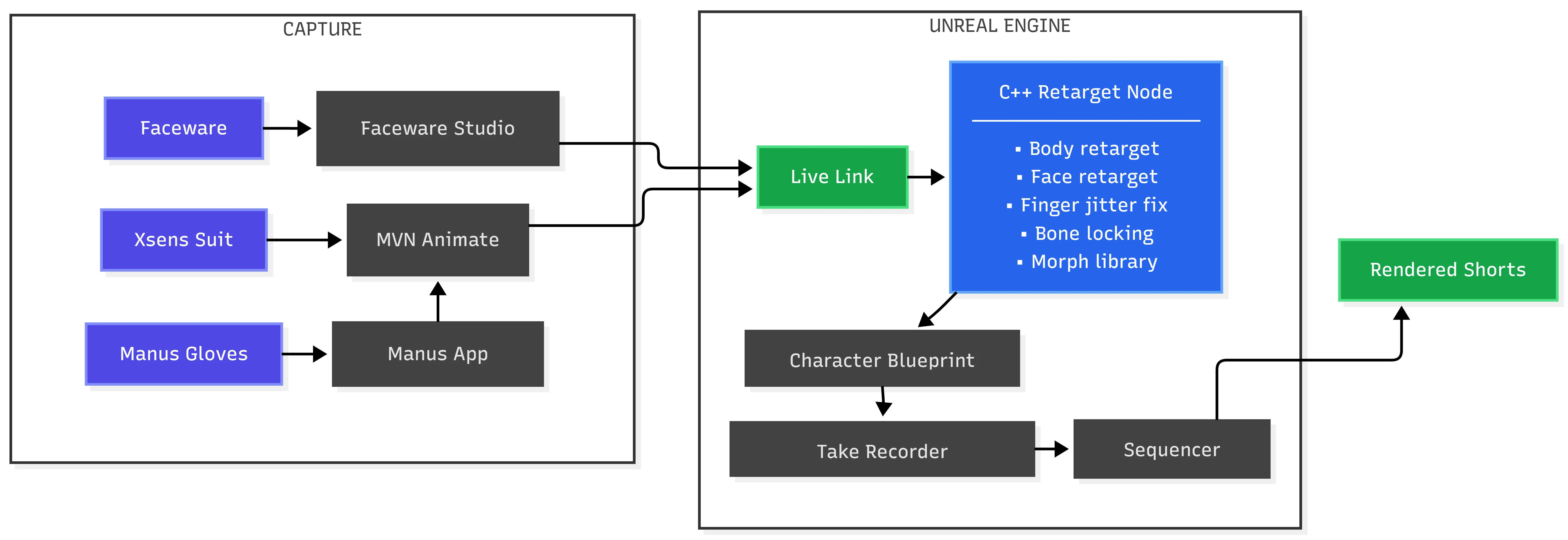
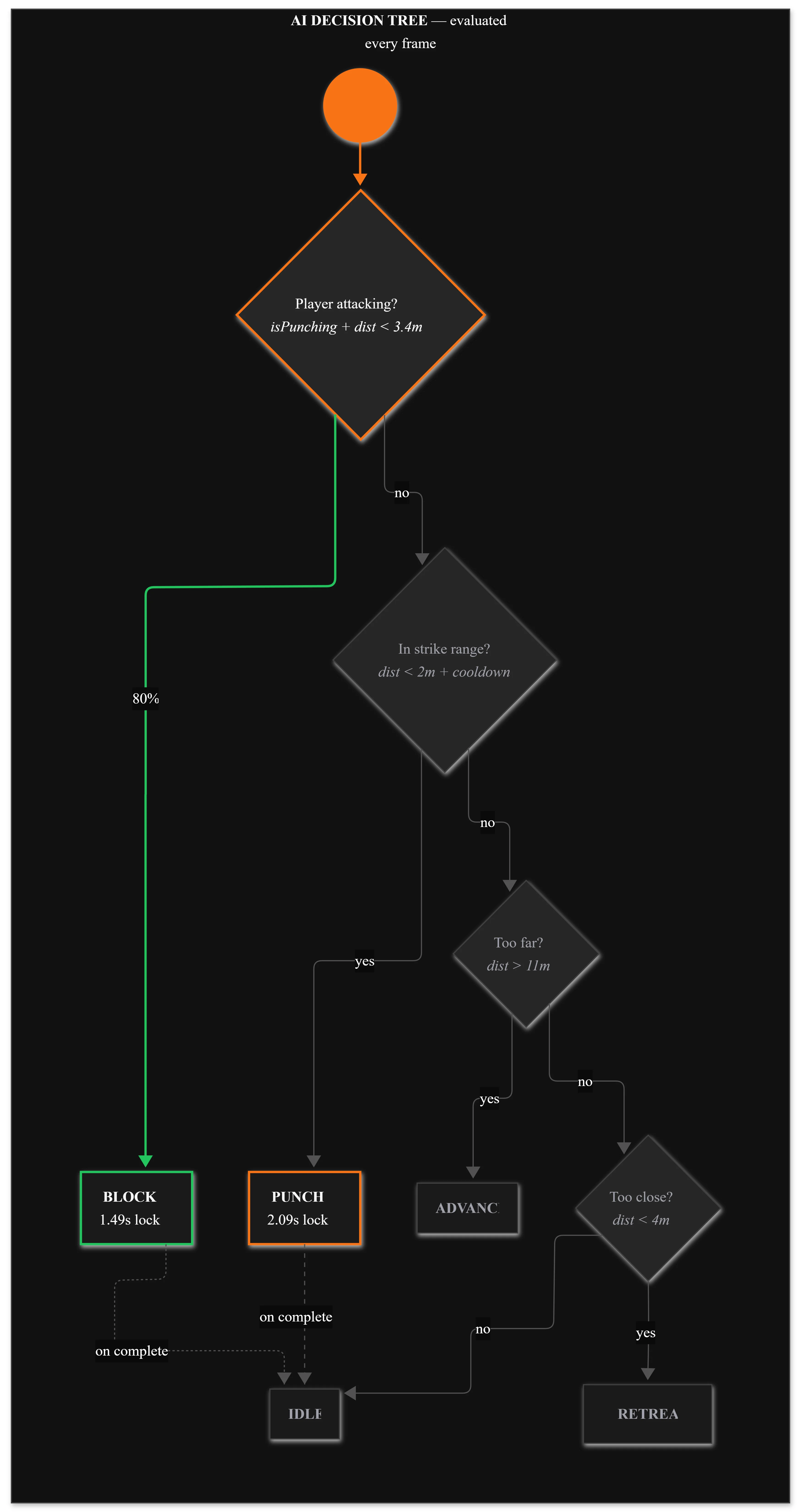
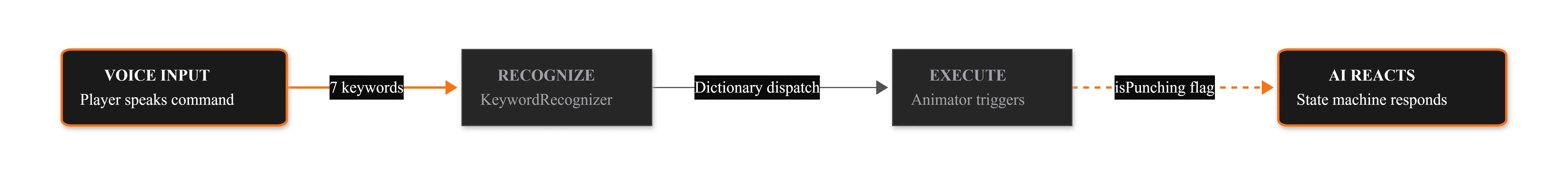
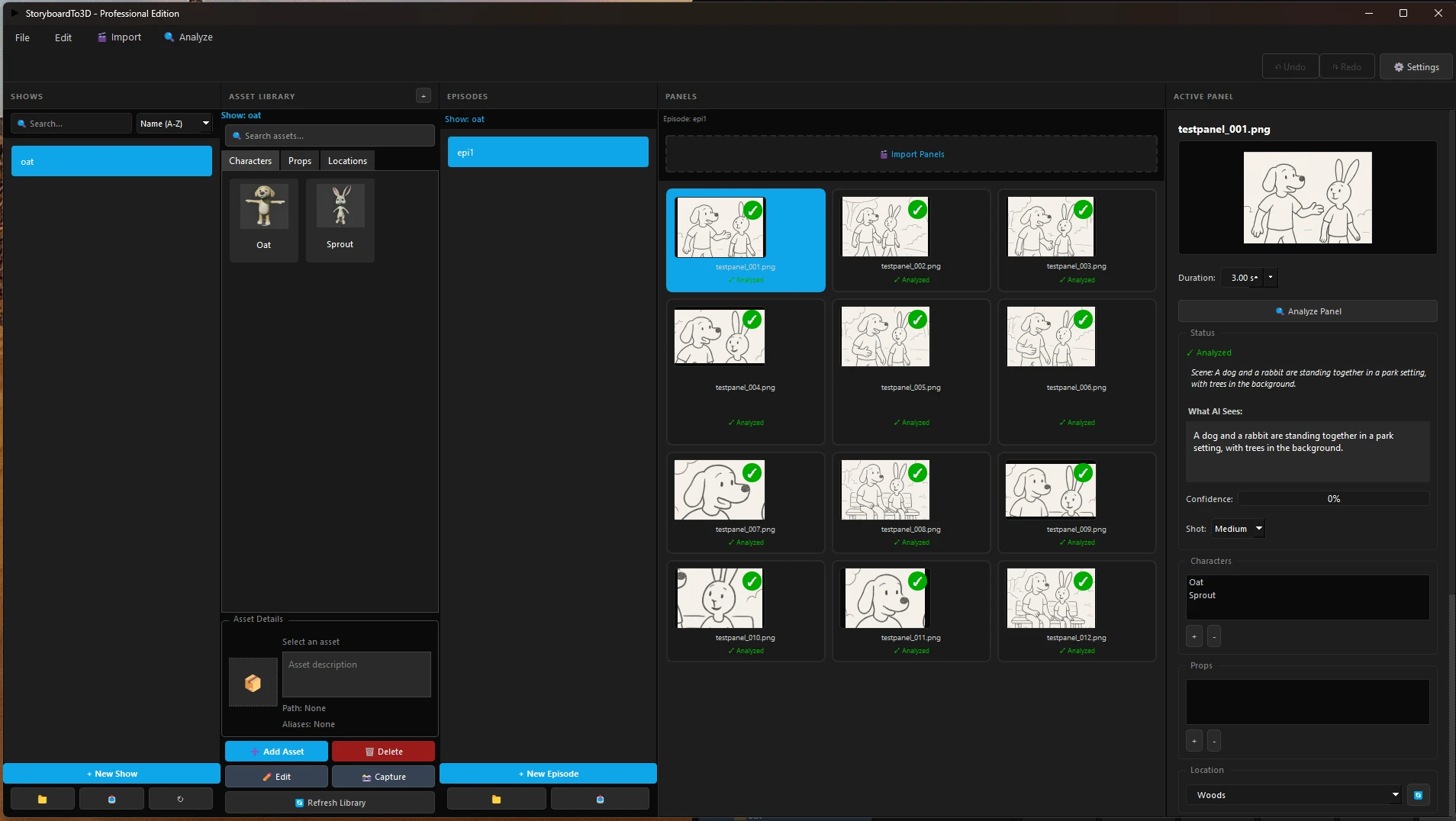
I built an Unreal Engine 5.6 plugin that automates storyboard-to-3D positioning using vision-language models. The system captures the scene from 7 camera angles to catch spatial errors invisible from a single viewpoint.
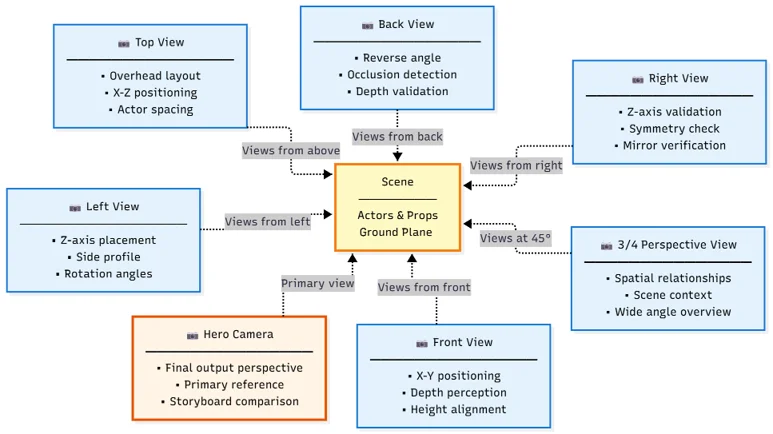
7-camera array captures scene from multiple angles to detect spatial errors
Multi-Angle Capture
7-camera array catches depth errors, occlusion, rotation problems that single-view misses
Iterative Refinement
AI analyzes render, proposes adjustments, refines until 80% match or max iterations
Multi-Provider
Supports Claude, GPT-4o, and LLaVA-13B with runtime switching
Unattended
Start it and come back to completed scenes. 7.8 to 69 minutes per panel depending on model.
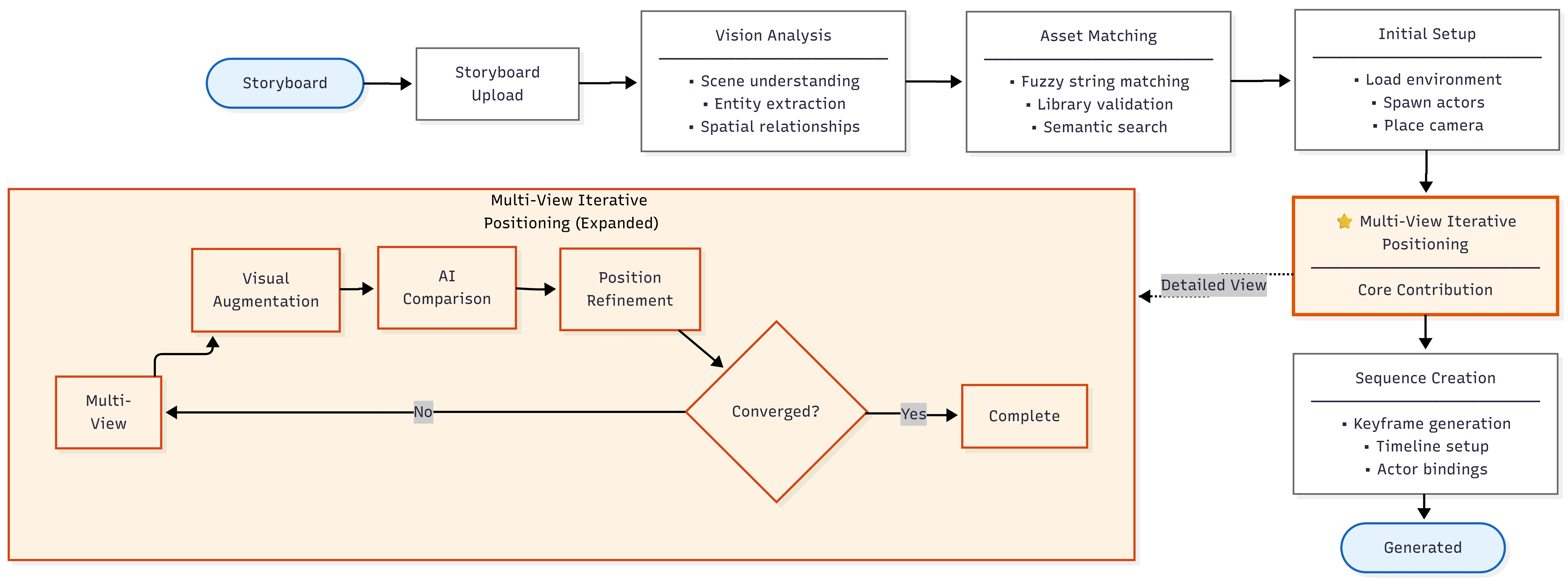
Full pipeline: storyboard → detection → positioning → validation loop
My Research Discovery: AI Score Hallucination
37.2%
gap between what AI says it scored vs what it actually got
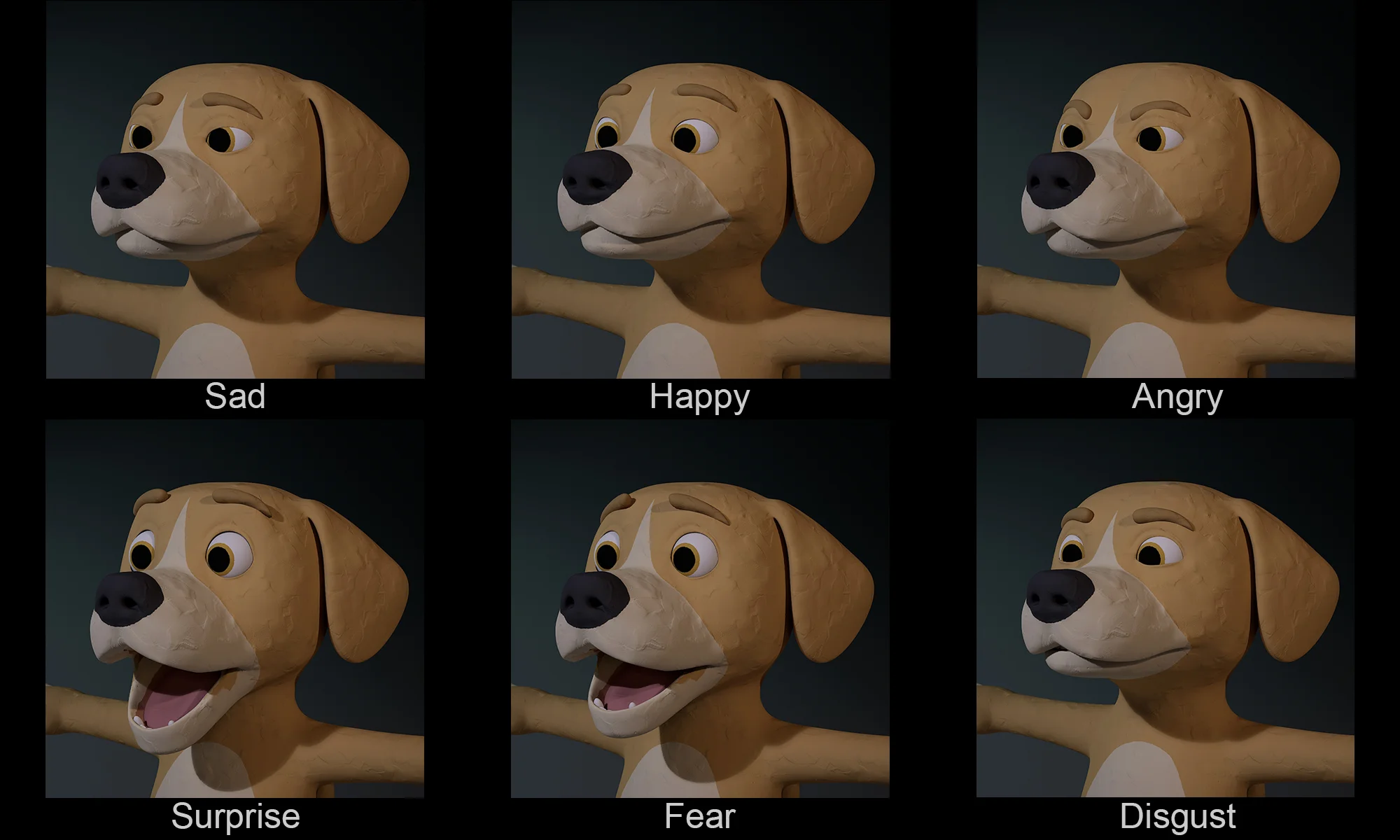
All three models reported ~84% confidence on average, but actual success ranged from 16% to 83%. The AI thinks it did well when it didn't.
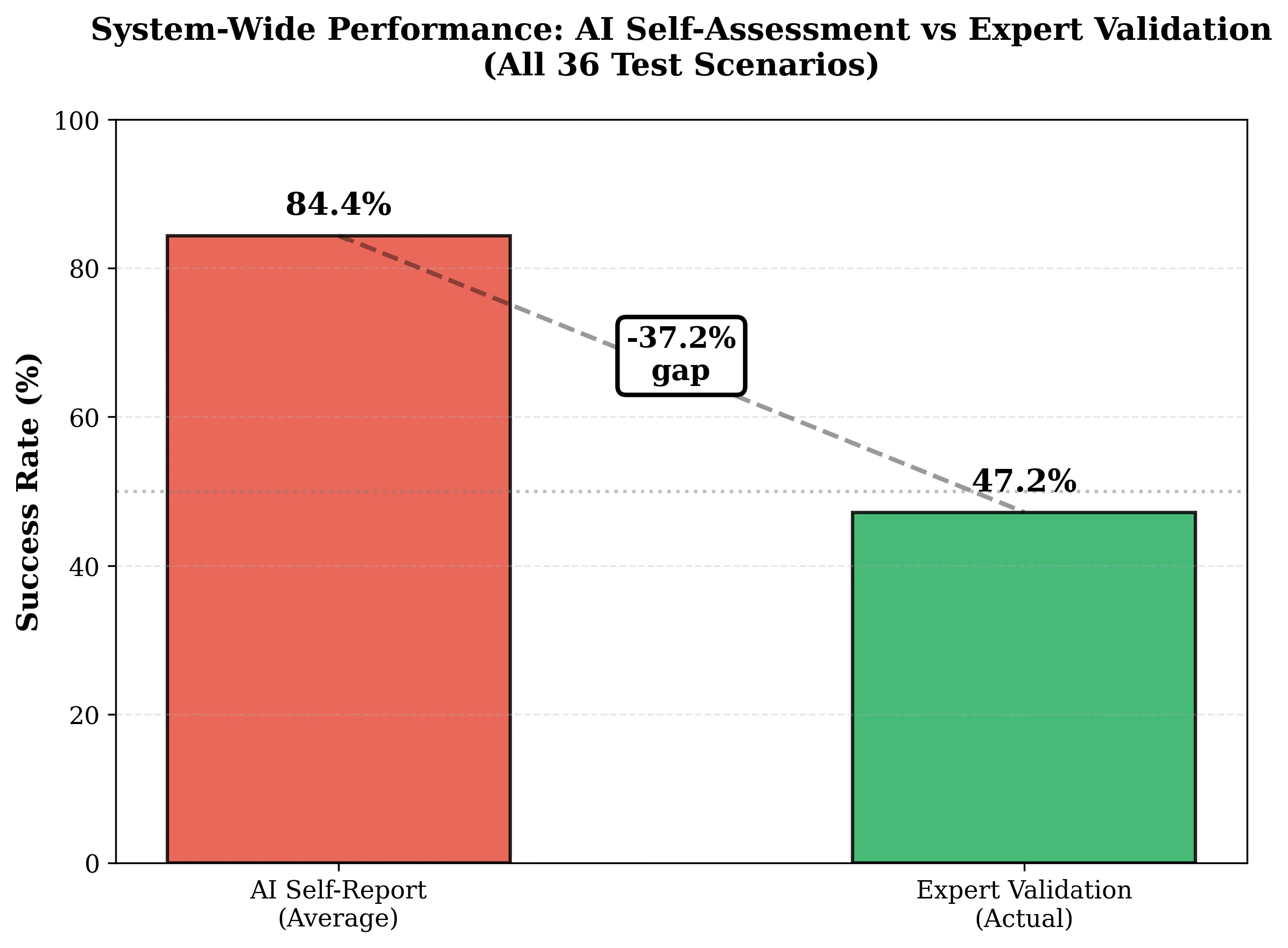
My testing: confidence vs accuracy across 12 panels per model (36 total scenarios)
My Test Results
83.3%
Claude Sonnet 4.5
+1.5% calibration error
Near-perfect calibration
41.7%
LLaVA-13B
+42.9% calibration error
Free, local inference
16.7%
ChatGPT-4o
+67.1% calibration error
Severe overconfidence
What I Learned
I found that all three models reported nearly identical confidence (~84%), but actual success ranged from 16.7% to 83.3%. GPT-4o would say "nearly perfect positioning" on scenes that were completely wrong. Claude's extended thinking let it recognize its own failures, which turned out to be critical for getting usable results.
My thesis committee recommended I submit to SIGGRAPH 2026. This AI Score Hallucination finding applies beyond this specific tool. If you're building anything that trusts AI to grade its own work, you need to account for this.
Built With
Unreal Engine 5.6
C++
Python
Claude API
GPT-4o API
LLaVA-13B
Ollama